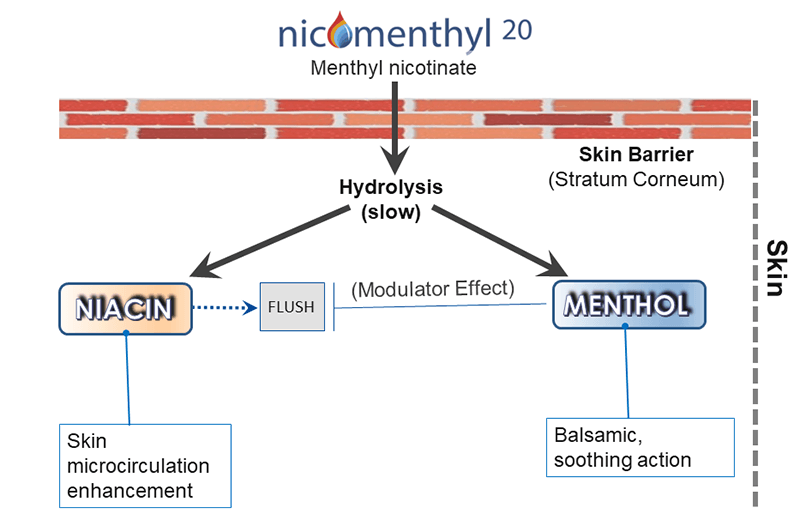
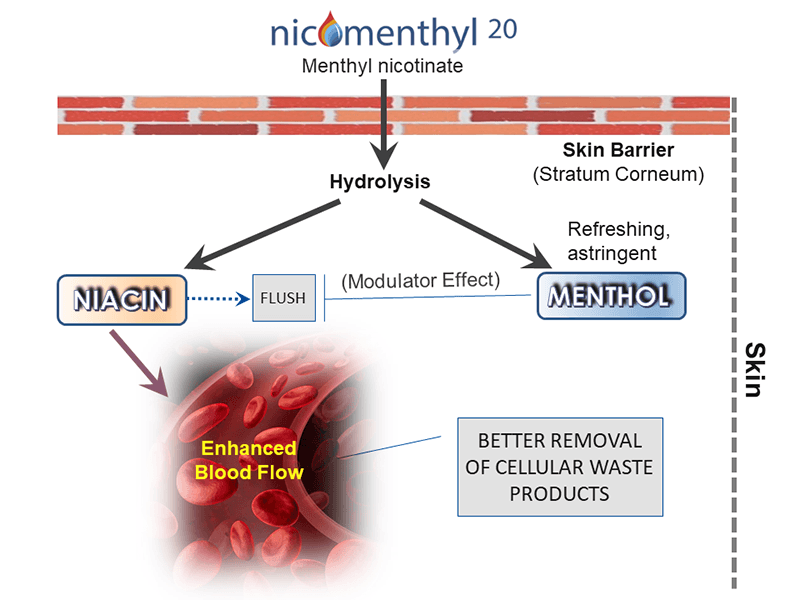
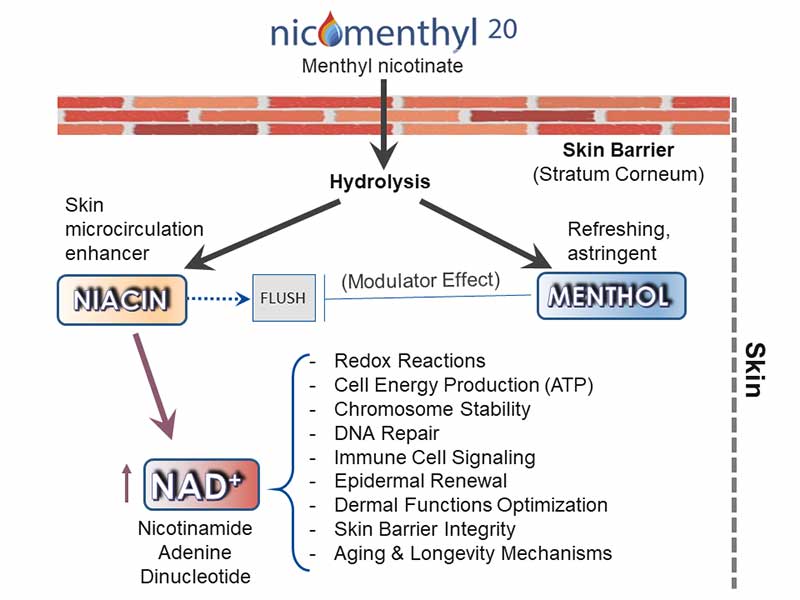
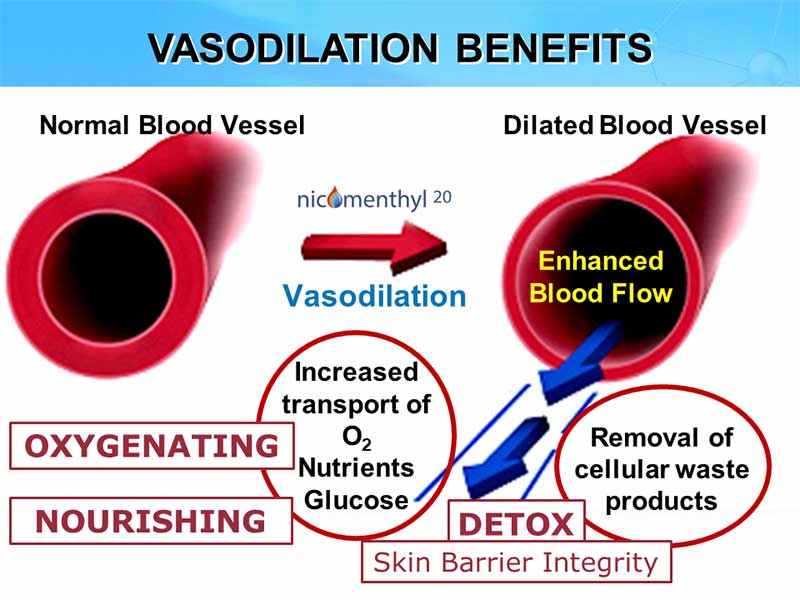
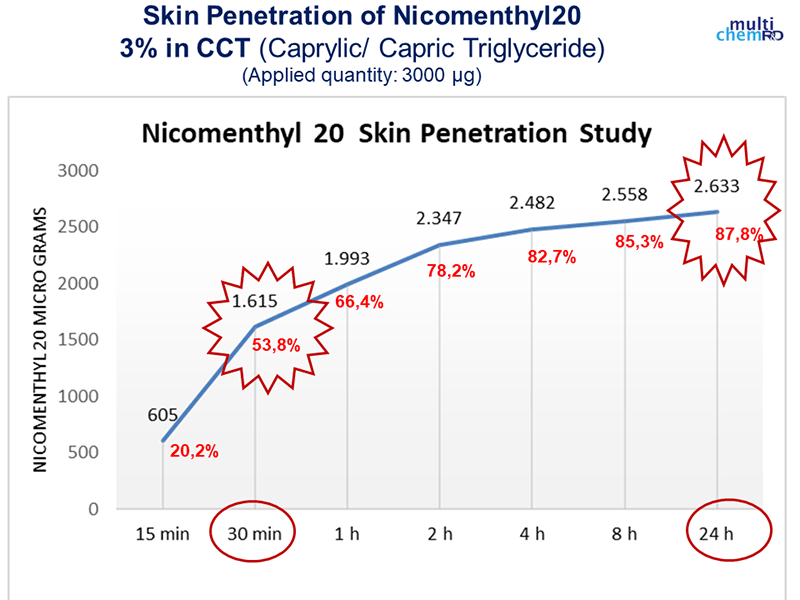
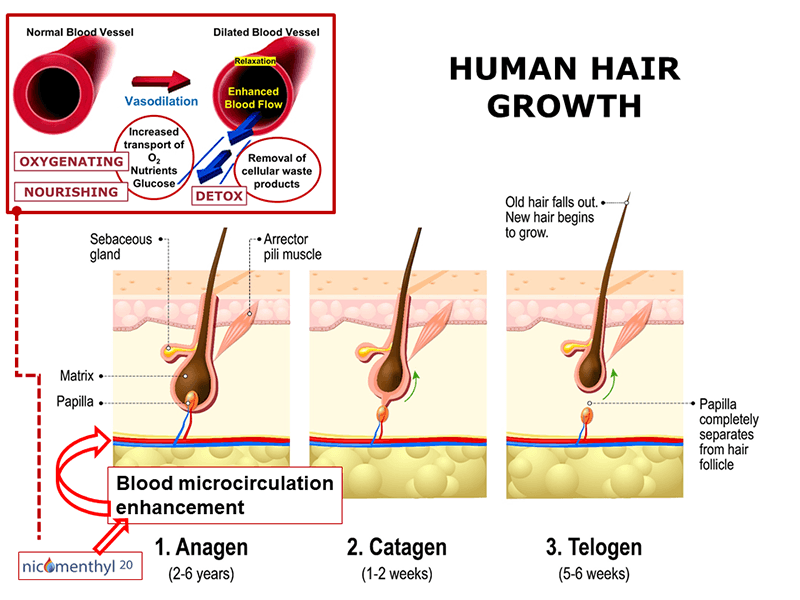
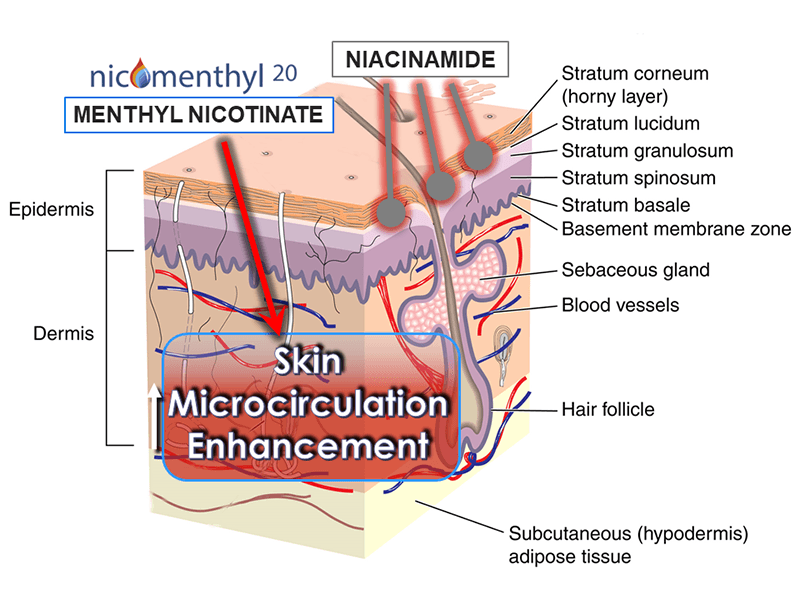
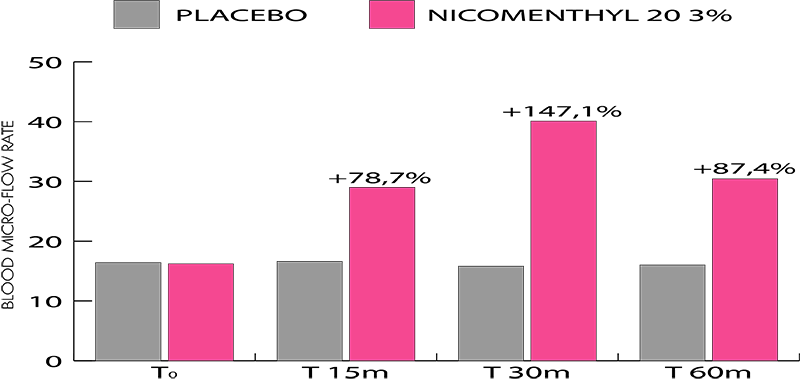Yes. What was previously called “Nicomenthyl” is now named “Nicomenthyl 20”.
Nicomenthyl 20 is the same substance (menthyl nicotinate: purity >99%), same CAS number (40594-65-8), same INCI name, same chemical & physical properties, same grade, same technical characteristics as the previous substance named Nicomenthyl.
The trademark Nicomenthyl® at first represented a single product; however, during the years, it has evolved into a range comprising 2 other cosmetic products, both of them based on menthyl nicotinate (i.e. Nicomenthyl Cool & Nicomenthyl Hot). To better differentiate the original Nicomenthyl from these new products, it was chosen to give the original pure molecule (menthyl nicotinate) the name Nicomenthyl “20”, with reference to the date 2020, January 20, that’s to say when Multichem R&D had implemented a more advanced and innovative proprietary procedure to manufacture a fully deodorized menthyl nicotinate.