Published: March 23, 2020 - Cell Death & Differentiation volume 27, pages 1451–1454 (2020).
This article, published in the prestigious journal nature on March 2020, says:
- “…vitamin B3 (niacin or nicotinamide) is highly effective in preventing lung tissue damage [7]. It might be a wise approach to supply this food supplement to the COVID-19 patients…” (bold added)
- “…Vitamin B3 can be given to patients starting to have lung CT image abnormalities…”
- “We propose some simple, but largely ignored, approaches to the treatment of COVID-19 patients (Fig.1)... Since Vitamin B3 is highly lung protective, it should be used as soon as coughing begins..." (bold added)
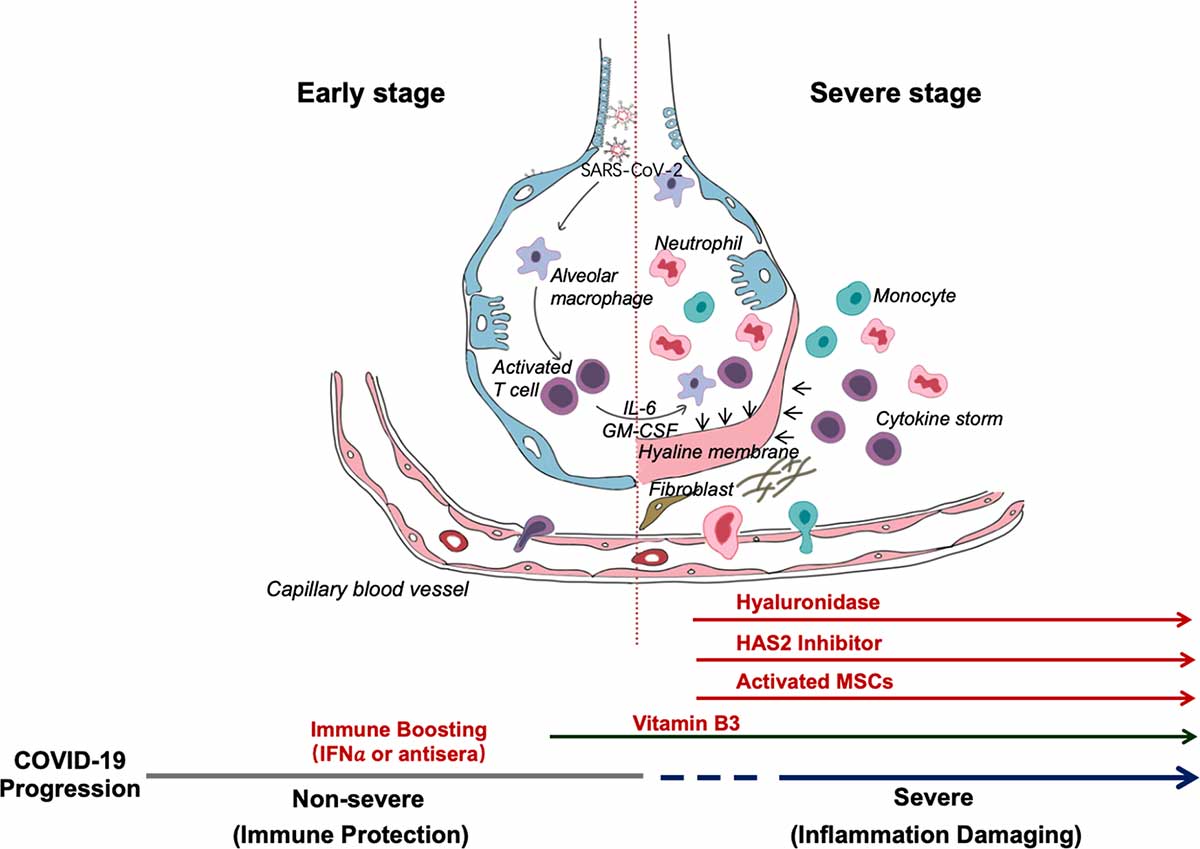
Fig. 1 - Schematic representation of the progression of COVID-19 infection and potential adjuvant interventions.
After an incubation period, the invading COVID-19 virus causes non-severe symptoms and elicits protective immune responses. The successful elimination of the infection relies on the health status and the HLA haplotype of the infected individual. In this period, strategies to boost immune response can be applied. If the general health status and the HLA haplotype of the infected individual do not eliminate the virus, the patient then enters the severe stage, when strong damaging inflammatory response occurs, especially in the lungs. At this stage, inhibition of hyaluronan synthase and elimination of hyaluronan can be prescribed. Cytokine activated mesenchymal stem cells can be used to block inflammation and promote tissue reparation. Vitamin B3 can be given to patients starting to have lung CT image abnormalities.