NICOMENTHYL® 20's efficacy against damages caused by BLUE LIGHT and WIFI radiations
NICOMENTHYL® 20 has shown to have a highly protective, repairing and detox effect not only against damages caused by UV rays, oxidative chemicals, urban particulates and cigarette smoke, but Blue Light and WiFi radiations as well.
Both these types of electromagnetic waves are produced by the common electronic devices, which people are particularly exposed to, sometimes much more intensively than usual, in the lockdown and/or smart working conditions induced by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Blue light is the blue-colored band of visible light with wavelength from 380 to 500 nm, irradiated from electronic devices – smartphones, tablets, computers and TVs. From recent scientific studies, these electromagnetic waves are known to generate “…free radicals and especially reactive oxygen species in human skin… in a manner similar to that caused by the infrared or ultraviolet irradiations, leading to the conclusion that also blue-violet light at high doses could represent a comparably adverse factor for human skin.”[1]
WiFi radiation is consisting of invisible radiofrequency radiation (RFR), in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency range (corresponding to wavelengths of either 12 cm or 6 cm), emitted by cellphones, computers, Bluetooth speakers, and other WiFi-powered devices.
A growing body of scientific literature evidences that this kind of radiofrequency radiation appears to act as a toxin to biological systems and “…has been shown to cause an array of adverse effects on DNA integrity, cellular membranes, gene expression, protein synthesis, neuronal function, the blood brain barrier, melatonin production, sperm damage and immune dysfunction.”[2]
Even though there is still much to research and verify in this field as to the extent of the skin damages and their long-term effects, it is well-known that they are caused through the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS).
Overproduction of ROS and RNS, generated by excessive exposure to Blue Light and WiFi radiation, allows the formation of free radicals that are the major cause of the oxidative stress. This latter one, in the long range, may weaken the epidermal barrier and accelerate the aging process, particularly when the subject is very close to the source of emission of the radiation itself.
A recent in vitro study on cultures of human keratinocytes has shown Nicomenthyl 20’s very significant protective and detoxifying efficacy against both, Blue Light and WiFi radiations.
In this study, the exposure of keratinocytes has been performed versus
- BLUE LIGHT diffused by LED lamps with an intensity of 5 mW/cm2 (TOPLANET 75W LED Pannel Grow Light Serie 2.0). The exposure was performed as follows
a) acute: 8 hours single exposure to Blue light irradiation
b) repeated: 3 cycles (2 hours each) of exposure to wireless radiations, every 24 hours. - WIFI emitted from a WiFi device with power -20.0 ± 5.0 dBM (D-Link DAP-1330 Range Extender - DAP-1330/E). The exposure was performed as follows
a) acute: 8 hours single exposure to wireless radiations
b) repeated: 3 cycles (2 hours each) of exposure to wireless radiations, every 24 hours.
The protective, detoxifying efficacy of Nicomenthyl 20 (menthyl nicotinate) has been tested considering these three experimental conditions:
- negative control (CTR-): untreated cultures of human keratinocytes.
- positive control (CTR+): cultures of human keratinocytes treated with damaging agents (Blue Light or WiFi).
- Cultures of human keratinocytes treated with 0.05% Nicomenthyl 20 corn oil solution and exposed to damaging agents (Blue Light or WiFi).
Cell detoxification efficacy of Nicomenthyl 20 was assessed by evaluating the activity of glutathione S-transferases (GST), a group of isoenzymes playing a pivotal role in detoxifying tissues. These enzymes protect cells from toxic compounds by connecting thiol groups of glutathione to these compounds, leading to their elimination.
The GST activity is expressed in nmol/mL/min.
Results
Nicomenthyl 20 shows a marked detoxifying effect, as observed assessing the enzymatic activity of the glutathione S-transferase (GST) when Blue Light and WIFI radiations were used as stress agents. Stressed keratinocytes, treated with Nicomenthyl 20, showed a significant recovery of GST activity, in both cases, practically restoring their basal levels (i.e. re-establishing treated keratinocyte GST values near to those of the untreated negative control CTR-).
GST activity variations of Nicomenthyl 20 treated keratinocytes in comparison to the untreated negative control CTR- and to the Blue Light positive stressed control CTR+, are shown in Figure 1.
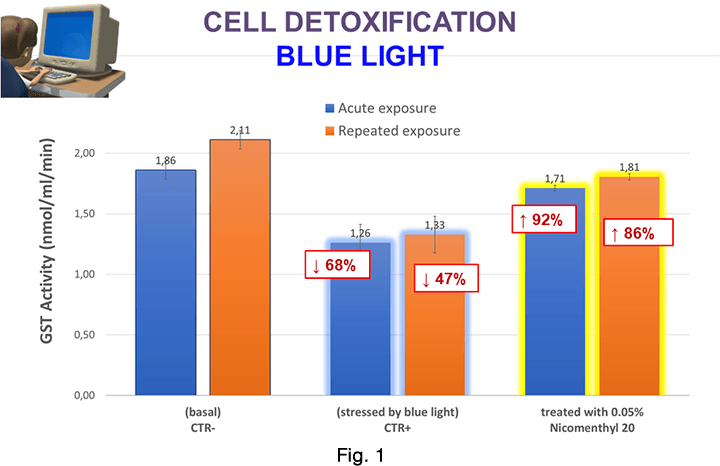
CTR- = negative control, basal untreated keratinocyte culture.
CTR+ = positive control, keratinocyte culture exposed to Blue Light. Acute exposure: 8 hours single exposure, causing a decline of GST activity down to 68% of basal value; repeated exposure: 3 exposure cycles of 2 hours each with 24 hours intervals, causing a decline of GST activity down to 47% of basal value.
Nicomenthyl 0.05% treated keratinocytes had a significant recovery of GST activity up to 92%, for acute exposure, and up to 86%, for repeated exposure, vs CTR- (basal condition)
GST activity variations of Nicomenthyl 20 treated keratinocytes in comparison to the untreated negative control CTR- and to the WiFi positive, stressed control CTR+, are reported in Figure 2.
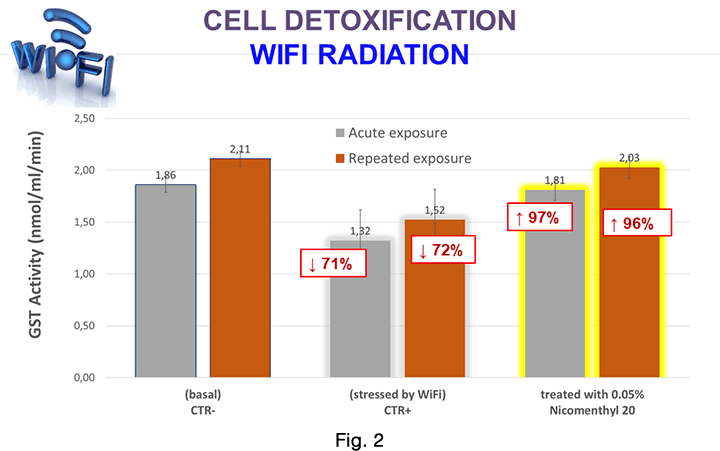
CTR- = negative control, basal untreated keratinocyte culture.
CTR+ = positive control, keratinocyte culture exposed to WiFi. Acute exposure: 8 hours single exposure, causing a decline of GST activity down to 71% of basal value; repeated exposure: 3 exposure cycles of 2 hours each with 24 hours intervals, causing a decline of GST activity down to 72% of basal value.
Nicomenthyl 0.05% treated keratinocytes had a significant recovery of GST activity up to 97%, for acute exposure, and up to 96%, for repeated exposure, vs CTR- (basal condition).
Conclusions
Nicomenthyl 20, a niacin (vitamin B3) lipophilic derivative and an effective NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) booster, significantly increases GST activity in human keratinocytes, both in single and repeated exposure conditions.
The results of this study clearly show that Nicomenthyl 20 exerts a significant skin protecting and stress-relieving action even against those damaging agents that represent one of the most elusive and controversial challenge of the ongoing COVID-19 era: BLUE LIGHT and WIFI radiations.
Download Formulation “Fresh as a Rose BlueLight & WiFi Detox Protective Spray”
References
- ⬆︎ Staffan Vandersee, Marc Beyer, Juergen Lademann, and Maxim E. Darvin. Blue-Violet Light Irradiation Dose Dependently Decreases Carotenoids in Human Skin, Which Indicates the Generation of Free Radicals - Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2015. Published online 2015 Feb 9. doi: 10.1155/2015/579675. Epub 2015 Feb 9.
- ⬆︎ Cindy L. Russell. 5 G wireless telecommunications expansion: Public health and environmental implications. Elsevier, 2018. doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.01.016
- Su G, Cai SJ, Gong X, Wang LL, Li HH, Wang LM. Establishment of a blue light damage model of human retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Genetics and Molecular Research. 2016 Jun 24. doi: 10.4238/gmr.15028092.
- Cora Roehlecke, Annette Schaller, Lilla Knels, and Richard H.W. Funk. The influence of sublethal blue light exposure on human RPE cells. Molecular Vision 2009; 15: 1929–1938. Published online 2009 Sep 21;15:1929-38.
- Liebmann J, Born M, Kolb-Bachofen V. Blue-light irradiation regulates proliferation and differentiation in human skin cells. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 13 August 2009; doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.194.
- Miller AB, Sears ME, Morgan LL, Davis DL, Hardell L, Oremus M, Soskolne CL. Risks to Health and Well-Being From Radio-Frequency Radiation Emitted by Cell Phones and Other Wireless Devices. Frontiers in Public Health. 2019 Aug 13. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2019.00223